Introduction
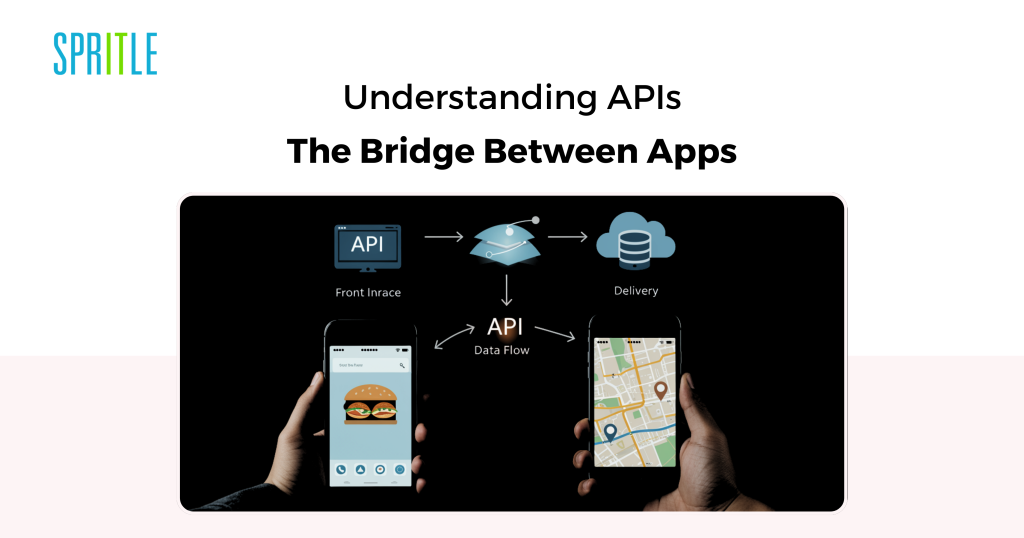
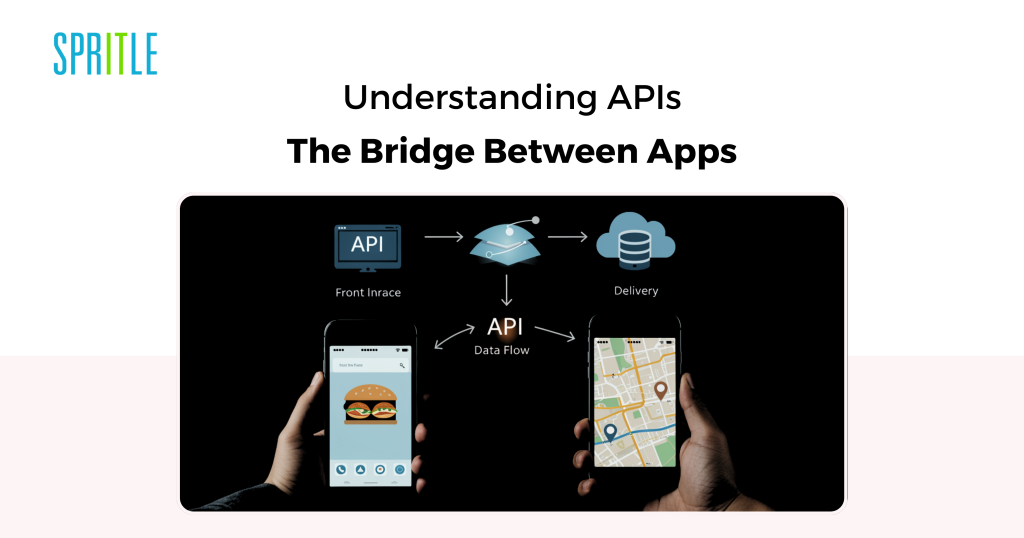
APIs, or Utility Programming Interfaces, are the invisible connectors that permit completely different software program methods speak to one another.They make it doable for apps to share information, carry out actions, and ship seamless consumer experiences.Whether or not you’re ordering meals or checking maps, APIs are working behind the scenes.On this weblog, we’ll discover what APIs are, how they work, and why they matter.By the tip, you’ll have a transparent understanding of how APIs energy the apps we use day by day.
What’s an API ?
- API expands as Utility Programming Interface.
- API (Utility Programming Interface) is a algorithm and protocols that enable completely different software program purposes to speak with one another. It acts as an middleman, enabling one program to request information or providers from one other.
- It’s the approach of communication between two purposes the place apps might differ of their platforms or when it comes to know-how.
As an example: Entrance-end of the app -> center layer (API) -> Again-end of the app
The center layer is used for each fetching information from the backend and inserting front-end information into the backend.
EXAMPLE: Think about you order meals on Swiggy or Zomato, and you’ll see the supply accomplice shifting on the map. Google Maps API acts like a helper, giving Swiggy/Zomato all the situation and route particulars they should maintain you up to date.
Kinds of API :
We will categorize APIs into many classes, however most often, APIs are categorized into two varieties: SOAP and REST.
- SOAP (Easy Object Entry Protocol) -> helps solely XML information
- REST (Representational State Switch) -> helps many codecs like XML, JSON, HTML
Each are internet providers. (An API on the web is known as an online service, and all internet providers are APIs.)
An internet service is an API wrapped in HTTP. An internet service wants a community, whereas an API doesn’t want a community for its operation.
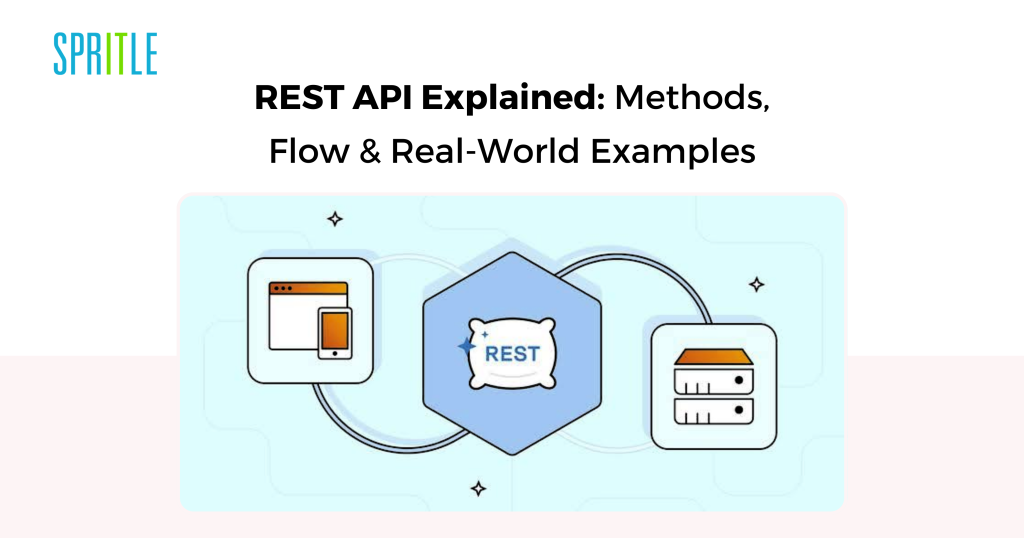
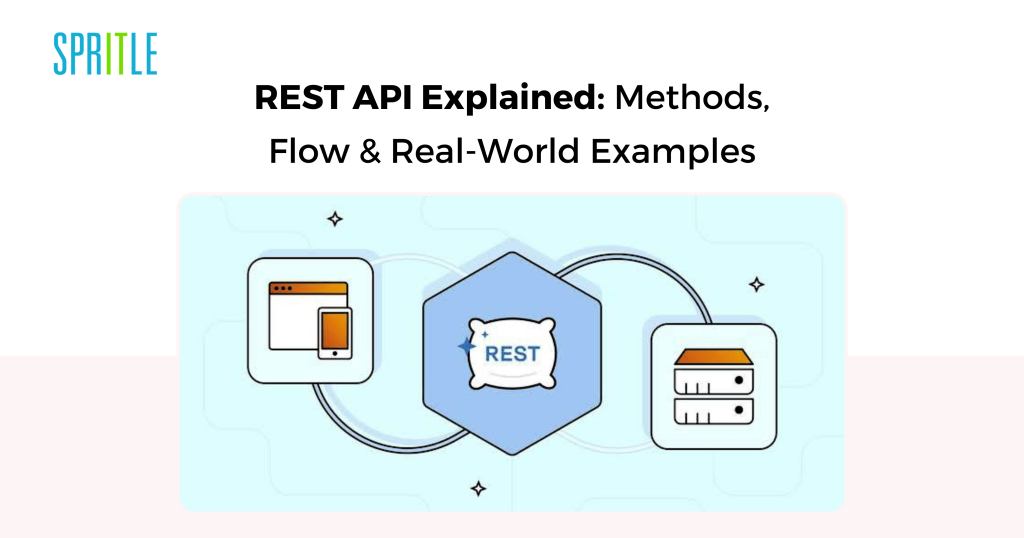
Understanding REST API
- REST API (Representational State Switch API) is a kind of internet API that follows the rules of REST, an architectural type for designing networked purposes.
- REST APIs use normal HTTP strategies to permit communication between a shopper (e.g., your browser or app) and a server.
- HTTP strategies are (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE). We will additionally establish it as CRUD operations (Create, Learn, Replace, Delete).
That is how REST APIs work: Request Message -> API -> Response Message.
Instance: Whereas we’re trying to find lodges on some web site, it’s the GET technique; ordering meals is the POST technique; altering the meals is the PUT technique; and cancelling the order is the DELETE technique.
Shopper vs Server: What’s the Distinction?
- A shopper is any gadget, software program, or utility that makes requests to a server to entry or work together with sources or providers. A shopper is usually a browser or {hardware} gadget that accesses a service made by a server.
The shopper is usually the user-facing element in a client-server structure.
- A server is a robust laptop or software program system that gives providers, sources, or information to different computer systems or shoppers over a community.
It handles requests from shoppers (similar to browsers or apps), processes them, and sends again the required response or information.
Shopper -> Web -> Server
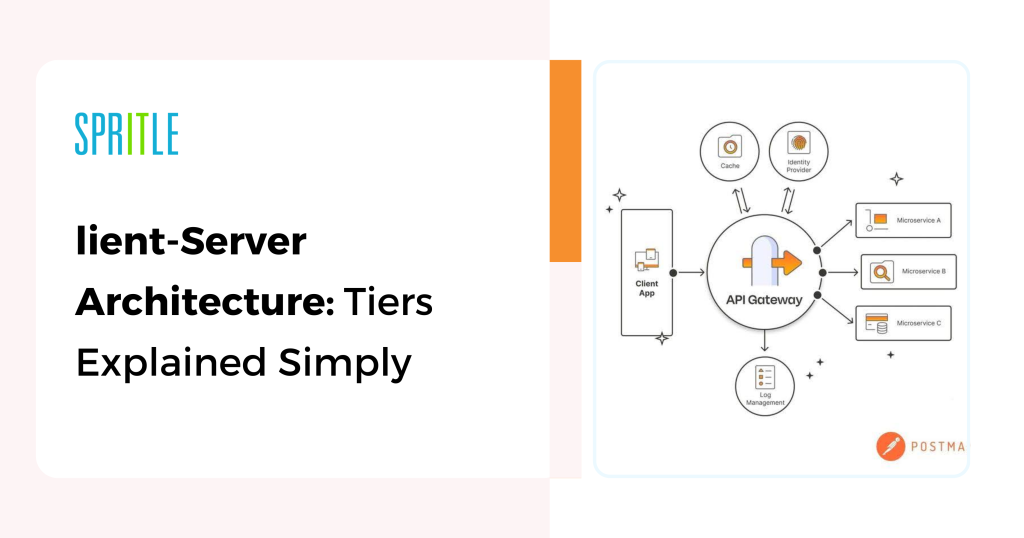
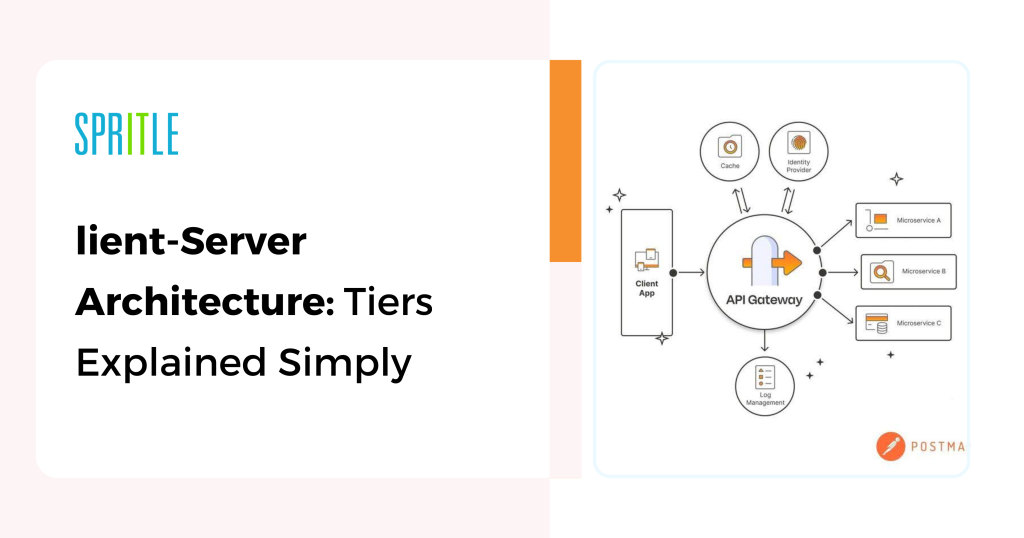
CLIENT / SERVER ARCHITECTURE :
Shopper-Server Structure is a mannequin utilized in networking the place two distinct entities, the shopper and the server, work together to supply providers or sources.
The structure is categorized as One-Tier Structure, Two-Tier Structure, Three-Tier Structure, and N-Tier Structure.
One-Tier Structure (Single-Tier):
- The shopper and the server are on the identical machine or in a quite simple setup the place the shopper accesses a neighborhood server.
- (Instance: An area database utility.)
Two-Tier Structure:
- The shopper interacts immediately with the server. That is the most typical mannequin.
- (Instance: An internet browser interacting with an online server.)
Three-Tier Structure:
- The structure is split into three layers: Presentation Layer (Shopper), Utility Layer (Server), and Database Layer (Information Storage). The shopper communicates with the appliance server, which in flip communicates with the database server.
Instance: An internet utility the place the shopper interacts with an online server, and the server communicates with a database to fetch information.
Presentation Layer (HTML, CSS, JS) → Utility Layer (Java, Python, C++, C#) → Information Layer (MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB)
N-Tier Structure:
An extension of the three-tier mannequin, the place there may be a number of intermediate layers for dealing with particular duties (e.g., a separate authentication server, enterprise logic server, and so forth.).
(Instance: Massive-scale enterprise purposes with a number of specialised servers
Understanding API Terminologies: URI, URL, and URN
The essential terminologies we have to learn about are URI, URL, and URN.
URI (Uniform Useful resource Identifier):
A URI is a novel string of characters used to establish a useful resource on the web or inside a system.
It supplies a solution to reference or find a useful resource, whether or not it’s a webpage, picture, file, or another sort of knowledge.
Instance: “http://google.com/articles/articlename” – Google.com alone is the URI (simply an identifier of the area).
URL (Uniform Useful resource Locator):
A URL is a particular sort of URI that not solely identifies a useful resource but additionally supplies the means to find it on the web.
It consists of each the deal with of the useful resource and the protocol used to entry it.
Instance: “http://google.com/articles/articlename” – The entire URL (full deal with with protocol and area).
URN (Uniform Useful resource Identify):
A URN is a particular sort of URI that uniquely identifies a useful resource by title inside a selected namespace, with out offering the situation or technique of accessing that useful resource.
In contrast to a URL, a URN doesn’t embody the deal with or protocol to entry the useful resource. As an alternative, it supplies a novel identifier for the useful resource.
Instance: “http://google.com/articles/articlename” – articles/articlename is the URN, also referred to as the endpoint.
Options and Assets in APIs
Characteristic:
A characteristic typically refers to a particular attribute, performance, or functionality of a system, utility, or service.
Characteristic is the time period utilized in guide testing to check some performance.
Options are points that present worth to the consumer and outline the system’s conduct or what it may possibly do.
Instance: In a messaging app, options would possibly embody sending messages, creating teams, audio calls, and file sharing.
Useful resource:
A useful resource refers to any entity or object that may be accessed, manipulated, or interacted with inside a system. Within the context of APIs or internet providers, a useful resource sometimes refers to information or objects which can be made out there by means of an API and may be created, learn, up to date, or deleted.
Instance: Product could possibly be a useful resource accessible at: https://api.instance.com/merchandise
Payload in APIs
- Within the context of APIs and internet improvement, payload refers back to the information that’s despatched with an HTTP request or response.
- It’s the precise content material or message being transmitted from the shopper to the server (or vice versa), which is processed or utilized by the server or shopper.
Payload sometimes refers back to the physique of the HTTP request or response .
TYPES OF PAYLOAD
It’s primarily categorized into two varieties similar to Request Payload and Response Payload.
1.Request Payload: The information you ship within the physique of a request (e.g., when creating or updating a useful resource).
Instance: Sending JSON information in a POST request to create one consumer:
jsonCopyEdit{
"username": "johndoe",
"electronic mail": "john@instance.com"
}
2.Response Payload: The information despatched again within the physique of the response (e.g., when fetching information or affirmation of an motion).
Instance: Response Payload of beforehand created consumer:
jsonCopyEdit{
"standing": "success",
"message": "Person created efficiently"
}
Getting Began with Postman
- Postman is a well-liked API testing and improvement device that permits customers to ship requests (like GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) to APIs and think about the responses.
We will do the next issues in Postman:
- Creating and managing collections of API requests.
- Sending requests with customized headers, parameters, and physique information.
- Viewing responses in numerous codecs (JSON, XML, and so forth.).
- Automating exams with pre-defined scripts.
- After putting in Postman, there will probably be an choice named ‘Workspace’. A workspace is an space the place we keep information and save them.
- It will likely be saved to our logged-in Gmail ID.
Attempt to create one workspace, and whereas creating it, we have to choose which kind we would like and go together with the API Testing choice.


Collections in Postman
- In Postman, a group is a gaggle of API requests organized collectively. A set comprises plenty of folders and HTTP requests.
- Inside the gathering, we are able to create any variety of requests as per our requirement. (Requests are a form of file we are able to create to carry out HTTP requests.)
- We will embody pre-request and take a look at scripts, use setting variables, and share collections with groups for collaboration.
- We will create, edit, delete, and run the gathering.
- We will additionally create duplicate collections, and we are able to export it.
Main Requests we’re going to use within the assortment:
- GET – Retrieve the supply from the information.
- POST – Create useful resource on database.
- PUT – Replace current useful resource on database.
- Patch – Replace partial particulars of useful resource.
Delete – Delete current useful resource from the database.
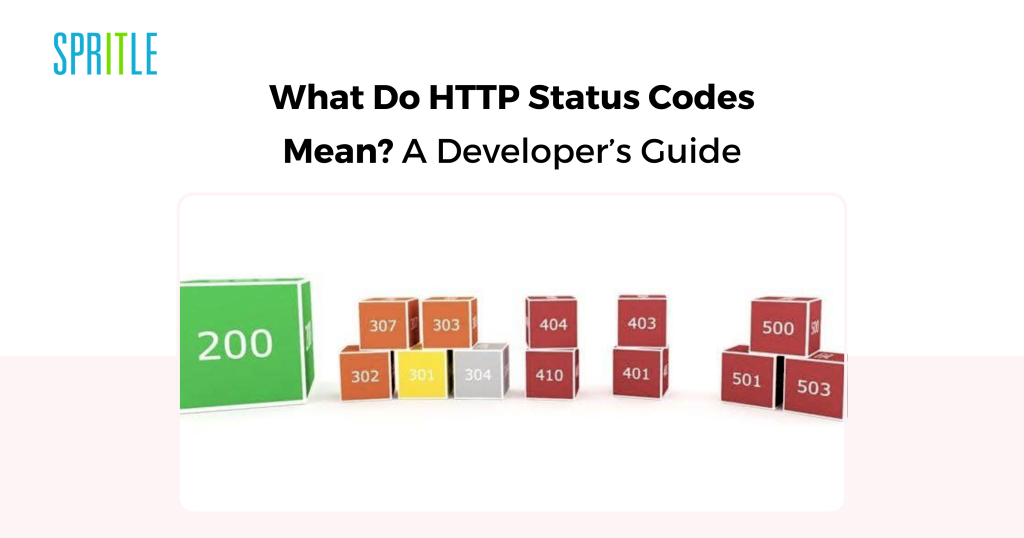
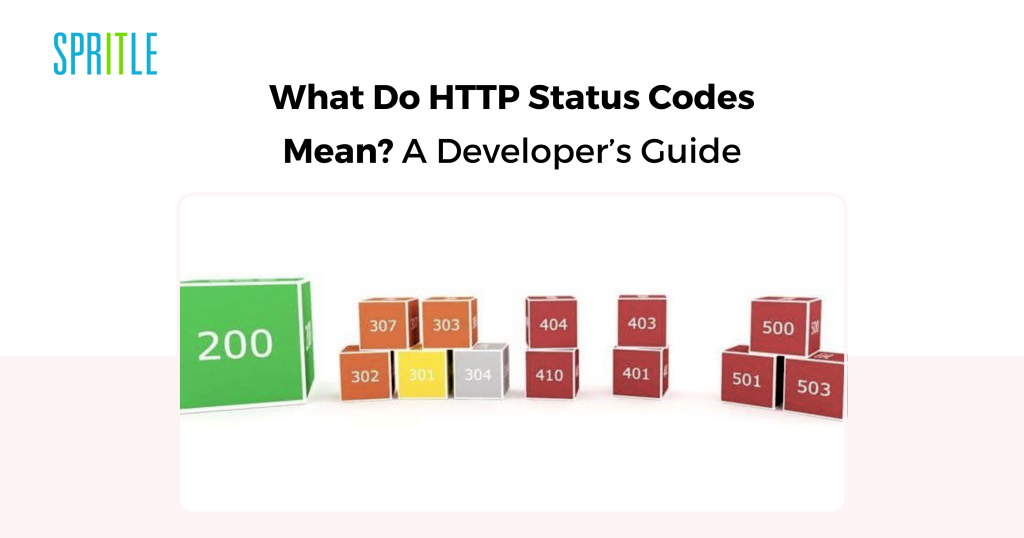
Understanding HTTP Standing Codes
A standing code is a three-digit quantity despatched by a server in response to an HTTP request. It signifies the results of the request and whether or not it was profitable, encountered an error, or requires additional motion.
200 Sequence:
200 – OK, 201 – Created, 202 – Accepted, 203 – Non-authoritative data, 204 – No content material
400 Sequence:
400 – Dangerous request, 401 – Unauthorized, 403 – Forbidden, 404 – Not discovered, 409 – Battle
500 Sequence:
500 – Inside server error, 501 – Not carried out, 502 – Dangerous gateway, 504 – Gateway timeout, 599 – Community timeout
Setting Up the Setting for API Testing
Pre-Requisites:
1.) NodeJS set up for making a customized API
- INSTALL NodeJS from its official web site.
- npm – Node Package deal Supervisor additionally comes with NodeJS.
- After set up, go to setting variables in your PC and examine whether or not the trail is configured or not.
- Additionally, run
node --versionwithin the CMD immediate to make sure its set up.
2.) Putting in JSON Server
- Run
npm set up -g json-serverin CMD.
- Create one JSON file with some JSON information in it. (This will probably be our customized API)
- Run that file in CMD as
json-server filename.
Then our customized API will run on localhost (you possibly can see the port in CMD), and we are able to carry out HTTP requests by way of Postman.
What’s JSON ?
JSON is expanded as JavaScript Object Notation.
- It’s a light-weight, text-based format used to symbolize structured information. It’s generally used for transmitting information between a server and a shopper in internet purposes, particularly in APIs.
- Mainly, it was designed for human-readable information interchange. It’s textual content, written with JavaScript notation.
- It’s prolonged from the JS language. Extension is .json
- Its web sort (MIME) is utility/json.
Terminologies:
- Strings needs to be written in double quotes and will need to have curly braces.
{"title":"jhon"} - For quantity information, we don’t want to surround it in double quotes.
{"age":30} - If we need to give two values for one key, then we’ve got to separate them with a comma (it’s an array). →
{"cellphone":[123,456]} - Boolean information doesn’t require quotations. →
{"boolean":false}.nulladditionally doesn’t require quotations. - Arrays might retailer primitives →
{"information":[1,2,3]}. And arrays having objects imply having all of the codecs like quantity and string.
Publish Response Use Instances:
This part comprises primary info and use instances about what we have to validate and know for Guide API Testing.
All of the use instances and scripts are going to be executed within the Publish-response tab within the ‘Scripts’ choice.
Issues we have to validate:-
- Standing Code
- Headers
- Cookies
- Response Time
- Response Physique
Preliminary Stage Validations and Use Instances:
Take this URL for example: https://reqres.in//api/customers?web page=2
‘’https://reqres.in’’ –> Host or Area
‘’api/customers?’’ –> Path Parameters
‘’web page=2’’ –> Question Parameters (after the query mark is named a question parameter)
‘’2’’ –> Useful resource
In Postman, whereas sending requests in JSON format (inside the gathering), we have to choose the ‘Uncooked’ choice underneath the Physique part.
pm – It’s a Postman library that we’re going to use to write down scripts.
To jot down a take a look at script in Postman, we’ve got two widespread features: Regular Perform and Arrow Perform.
Regular Perform Syntax:
javascriptCopyEditpm.take a look at("Take a look at Identify", perform() {
// assertion;
});
Arrow Perform Syntax:
javascriptCopyEditpm.take a look at("Take a look at Identify", () => {
// assertion;
});
Within the “Take a look at Identify” subject, we are able to write our required texts associated to the motion we’re going to carry out.
Within the “assertion” subject, we’re going to write the precise script.
We are going to use this syntax within the Postman Scripts choice whereas utilizing HTTP requests in a group.
1.Testing the only standing code :-
javascriptCopyEditpm.take a look at("standing code is 200", () => {
pm.response.to.have.standing(200);
});
This syntax will take a look at whether or not the HTTP response will return 200 because the standing code or not.
We will change the standing code as per our requirement rather than ‘200’.
2.Testing a couple of standing code :-
javascriptCopyEditpm.take a look at("profitable put up request", () => {
pm.count on(pm.response.code).to.be.oneOf([200, 201]);
});
This syntax will take a look at whether or not the HTTP response will return both 200 or 201.
3.Testing Standing Code Textual content :-
javascriptCopyEditpm.take a look at("standing code is 200", () => {
pm.response.to.have.standing("created");
});
It is going to examine if the textual content of the standing code is ‘created’ or not.





