The Common Knowledge Safety Regulation (GDPR) stands as a gold normal for knowledge safety legal guidelines globally, setting stringent benchmarks for privateness and knowledge safety. Not too long ago, India joined the league of nations with sturdy knowledge safety frameworks by enacting the Digital Private Knowledge Safety Act (DPDP) 2023. This laws marks a major step in India’s knowledge safety journey, aiming to stability world compliance with the nation’s distinctive socioeconomic panorama.
For organizations working underneath each frameworks or navigating India’s new regime, understanding the similarities and variations between GDPR and DPDP is crucial for compliance and strategic alignment. Let’s perceive intimately.
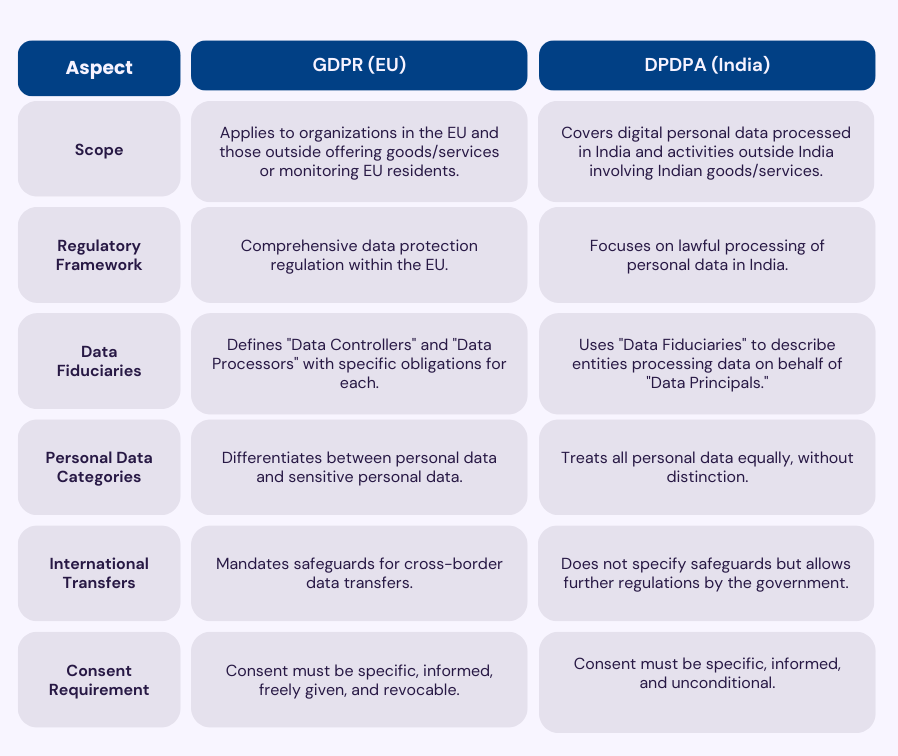
GDPR Vs. DPDP Act:
Scope and Applicability
Each the GDPR and DPDP Act prolong their jurisdiction past their geographical boundaries, concentrating on entities dealing with knowledge of people inside their territories or providing items and companies to their residents.
Key Variations:
- GDPR: Covers all types of private knowledge, whether or not digital or non-digital, offered they’re a part of a structured submitting system.
- DPDP Act: Limits its scope to digital private knowledge, together with offline knowledge digitized for processing, however excludes purely offline data.
Definitions and Categorization
GDPR categorizes knowledge into basic private knowledge and delicate classes (e.g., well being, faith, biometrics), with enhanced safeguards for the latter. DPDP lacks such categorization, making use of uniform requirements throughout all private knowledge varieties.
Each legal guidelines outline consent as knowledgeable, particular, and affirmative. Nevertheless, the DPDP Act introduces the time period “unconditional” to emphasise person empowerment additional.
Key Stakeholders
Generally known as “Knowledge Topics” underneath GDPR and “Knowledge Principals” within the DPDP Act, each frameworks prioritize particular person rights over knowledge. GDPR provides broader rights, similar to knowledge portability and resistance to automated decision-making, which aren’t explicitly offered underneath DPDP.
- Entities Processing Knowledge:
- GDPR’s Knowledge Controllers correspond to DPDP’s Knowledge Fiduciaries, emphasizing belief and accountability.
- Each acknowledge Knowledge Processors however differ in obligations—GDPR imposes direct tasks, whereas DPDP locations compliance accountability on the fiduciary.
Grounds for Processing
GDPR provides a number of lawful bases for knowledge processing, together with authentic pursuits and public curiosity. In distinction, the DPDP Act predominantly depends on consent, with exceptions like state features, authorized compliance, and emergencies. This narrower scope underneath DPDP prioritizes particular person management however could limit operational flexibility.
Revolutionary Options: Consent Managers
A singular side of the DPDP Act is the introduction of Consent Managers, entities facilitating clear and environment friendly consent dealing with. This characteristic is absent in GDPR, reflecting India’s deal with user-centric mechanisms to ease compliance and knowledge administration.
Compliance and Obligations
GDPR mandates complete notices for all knowledge processing situations. The DPDP Act limits this obligation to consent-based processing, with the added requirement of offering notices in native languages to boost accessibility.
GDPR requires breach reporting based mostly on danger evaluation, whereas DPDP mandates common notification of breaches to the Knowledge Safety Board and affected people, regardless of severity.
Cross-Border Knowledge Transfers
GDPR depends on adequacy choices, contractual clauses, and binding company guidelines to manage knowledge transfers. The DPDP Act adopts a centralized strategy, granting the Indian authorities authority to specify permissible nations, emphasizing sovereignty in knowledge governance.
Youngsters’s Knowledge Safety
The GDPR provides a versatile age threshold for parental consent, starting from 13 to 16 years. Conversely, the DPDP Act units the age of consent uniformly at 18 years, mandating parental oversight and proscribing practices like focused promoting to kids.
Penalties and Enforcement
Each frameworks impose stringent penalties for non-compliance, signaling critical penalties for knowledge breaches and violations. GDPR’s tiered penalty construction is predicated on turnover percentages, whereas DPDP enforcement particulars stay to be totally disclosed however point out a rigorous strategy.
GDPR vs. DPDPA
Abstract
The GDPR and DPDP Act share foundational rules of safeguarding private knowledge and selling accountability. Nevertheless, the DPDP displays India’s distinctive digital ecosystem, balancing world greatest practices with localized wants. Understanding their nuances permits organizations to tailor compliance methods successfully, fostering belief and innovation in an more and more data-driven world.
Guarantee seamless compliance with the DPDP Act! Contact us right now to find out how CryptoBind Options can simplify your knowledge safety journey and maintain your enterprise safe.




