In September 2020, I created the Switching, Routing, and Bridging Terminology video as a part of the How Networks Actually Work webinar. This weblog submit is a Whisper transcript edited/summarized by ChatGPT and polished by Yours Actually 😉
Whereas I’m constructive ChatGPT did an incredible job structuring the transcript and eradicating my verbal meandering, I ponder how far we obtained down the slippery slope towards AI slop. Your feedback are extremely appreciated. Thanks!
After discussing networking layers and addressing, it’s time to concentrate on transferring packets throughout a community. Distributors love to make use of ill-defined phrases like switching as an alternative of forwarding, routing, or bridging, so let’s begin with the terminology.
Connecting all related gadgets to a single cable would indubitably simplify any networking stack, however sadly, we’re nearly by no means that fortunate. We want gadgets within the community (usually with a number of interfaces) that carry out packet forwarding between finish nodes.
Once we mentioned networking layers, I discussed gadgets like hubs, repeaters, or media converters. These merely convert bits between totally different bodily media, like copper and fiber.
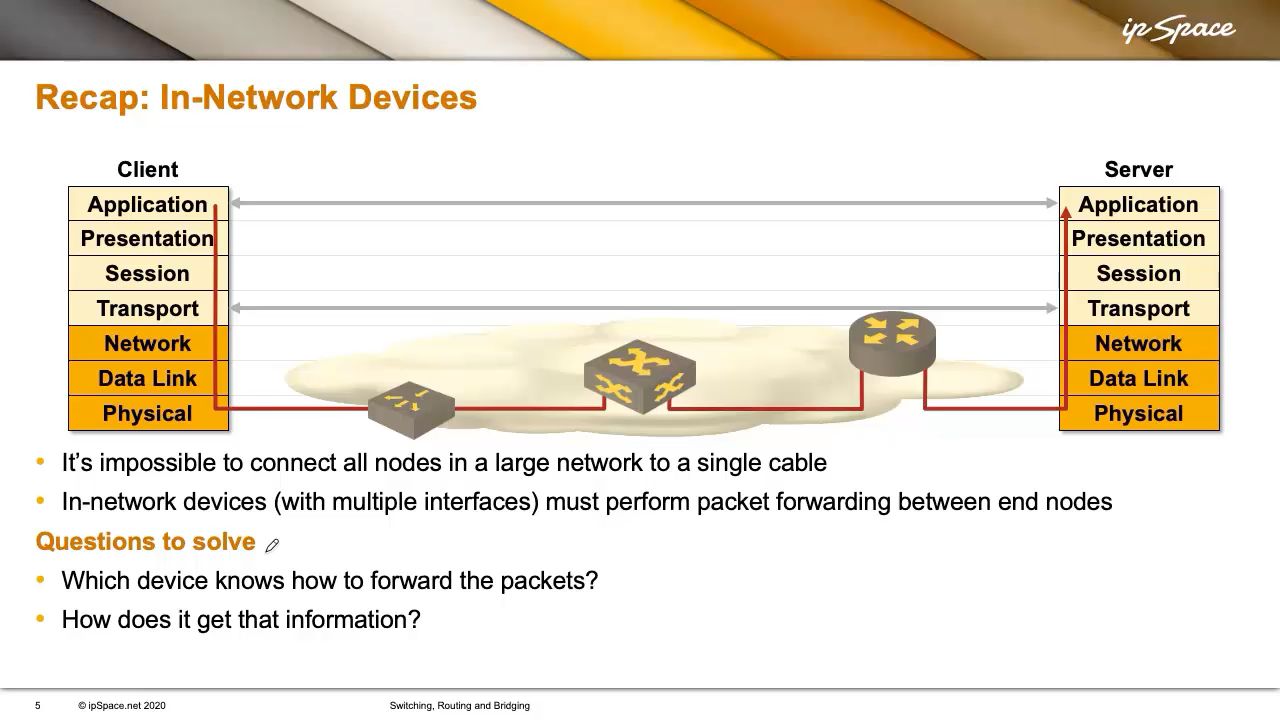
Subsequent, we’ve got gadgets that arguably shouldn’t exist: bridges. They join finish nodes on the knowledge hyperlink layer. However keep in mind, the information hyperlink layer is supposed to attach adjoining nodes. When you insert a bridge, the nodes are now not adjoining.
Lastly, we’ve got routers – Layer 3 gadgets that function on the community layer. Theoretically, any giant community (your private home Wi-Fi, a company LAN, or the worldwide Web) ought to use routers to interconnect segments.
Now that we all know which gadgets can carry out packet forwarding, let’s concentrate on two large questions:
-
Which system is aware of how one can ahead the packet?
In the event you’ve labored with IP, your intuition could be: “The router does!” However that’s just one forwarding paradigm. Generally, the sender determines the forwarding path—by deciding on a digital circuit, as an example—and gadgets within the community solely acknowledge these circuits. We’ll study at the very least three forwarding paradigms and establish which applied sciences, previous and current, use every.
For instance, section routing isn’t that totally different from source-route bridging in Token Ring. Nothing is really new in networking—we’ve simply reinvented concepts over time.
-
How does a tool know how one can ahead a packet?
No matter whether or not a tool is an finish node or an in-network system, it must get that info from someplace. It would guess, get it from a central controller, or study it from adjoining or non-adjacent gadgets.
The Three Planes of a Networking System
In any system that performs packet forwarding, there are three key planes:
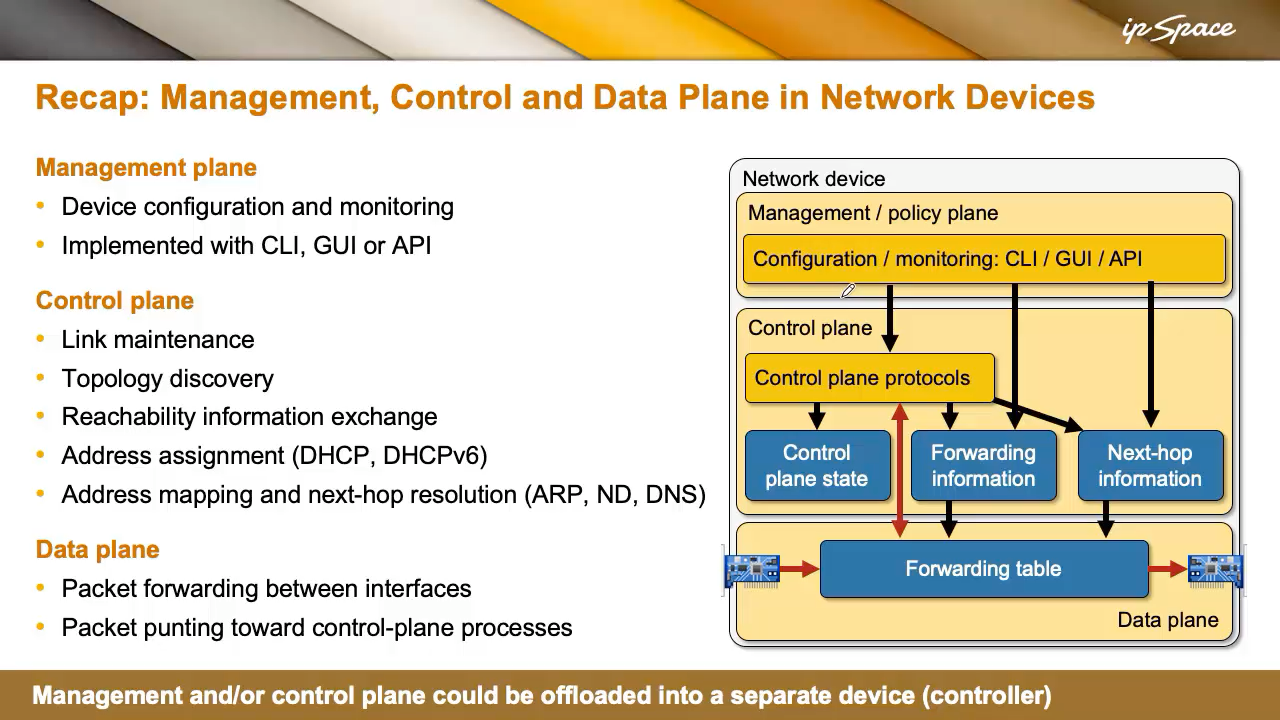
-
Information Aircraft: That is the place the precise forwarding occurs. The system makes use of a forwarding desk to find out how one can ship a packet, primarily based on info like MAC addresses, IP addresses, MPLS labels, and so forth.
If the information airplane can’t deal with the packet—maybe it’s too complicated or destined for the system itself—it’s punted to the management airplane.
-
Management Aircraft consists of processes operating within the system’s OS (usually Linux or one other Unix-based system). These processes deal with duties like:
- Hyperlink Upkeep (e.g., utilizing BFD)
- Topology Discovery (dealt with by routing protocols like OSPF or IS-IS)
- Deal with Task (e.g., DHCP, SLAAC)
- Deal with Mapping (e.g., ARP for IPv4, Neighbor Discovery for IPv6)
-
Administration Aircraft handles configuration and monitoring. Within the outdated days, we used console cables to configure gadgets. At present, many gadgets boot from the community and are managed through SSH, Telnet, or APIs.
An honest system ought to help at the very least a CLI and an API, so it may be managed manually or through automation instruments.
Routing Protocols and the Forwarding Desk
Routing protocols—like OSPF, IS-IS, or BGP—run within the management airplane. They:
- Construct inner topology or route databases.
- Calculate routing tables.
- Mix routing info with knowledge hyperlink layer mappings to create the forwarding desk.
This forwarding desk is what the information airplane makes use of to effectively ahead packets.
Layer-2 vs Layer-3 Forwarding (And Advertising Confusion)
There are two main methods to ahead packets throughout a community:
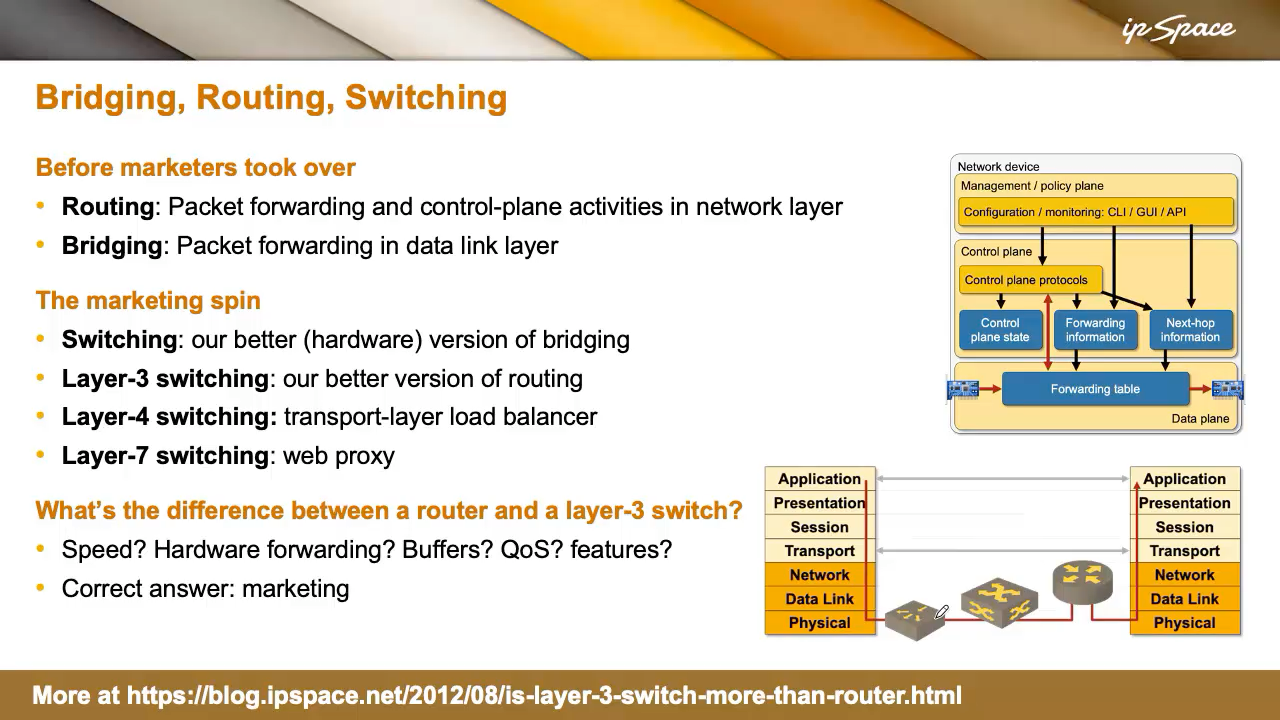
Early bridges did layer-2 forwarding in software program and barely managed to cope with two 10 Mbps Ethernet ports. When distributors started implementing bridging in {hardware}, they coined the time period switching to distinguish between hardware- and software-based bridges. Later, when Layer 3 forwarding grew to become quick sufficient in {hardware}, we obtained Layer 3 switching. It was all advertising—designed to place merchandise in opposition to bigger rivals like Cisco.
In actuality, what’s the distinction between a router and a Layer 3 swap? Simply advertising. Efficiency, buffers, or options don’t outline it. The label is determined by what the seller needs to name the system.
Terminology Clarification
On this webinar, I’ll attempt to use constant terminology:
- Switching = any packet forwarding.
- Layer 2 Switching = forwarding primarily based on MAC addresses.
- Bridging = often refers to clear Ethernet bridging.
- Layer 3 Switching = forwarding primarily based on IP addresses (IPv4 or IPv6).
- Routing = path choice and management airplane actions associated to IP forwarding.
Q&A Highlights
Q: Are there any management airplane actions at Layer 2?
A: Virtually none. Clear bridges don’t run management airplane protocols between themselves and finish nodes. They depend on dynamic MAC studying within the knowledge airplane. Protocols like STP present primary loop prevention however provide minimal discovery or routing.
Q: Isn’t all switching able to routing as we speak?
A: Not at all times. Excessive-end knowledge heart switches usually help full IP routing. However in campus or industrial environments, you’ll nonetheless discover switches that want separate licenses for routing or solely help bridging.
In September 2020, I created the Switching, Routing, and Bridging Terminology video as a part of the How Networks Actually Work webinar. This weblog submit is a Whisper transcript edited/summarized by ChatGPT and polished by Yours Actually 😉
Whereas I’m constructive ChatGPT did an incredible job structuring the transcript and eradicating my verbal meandering, I ponder how far we obtained down the slippery slope towards AI slop. Your feedback are extremely appreciated. Thanks!
After discussing networking layers and addressing, it’s time to concentrate on transferring packets throughout a community. Distributors love to make use of ill-defined phrases like switching as an alternative of forwarding, routing, or bridging, so let’s begin with the terminology.
Connecting all related gadgets to a single cable would indubitably simplify any networking stack, however sadly, we’re nearly by no means that fortunate. We want gadgets within the community (usually with a number of interfaces) that carry out packet forwarding between finish nodes.
Once we mentioned networking layers, I discussed gadgets like hubs, repeaters, or media converters. These merely convert bits between totally different bodily media, like copper and fiber.

Subsequent, we’ve got gadgets that arguably shouldn’t exist: bridges. They join finish nodes on the knowledge hyperlink layer. However keep in mind, the information hyperlink layer is supposed to attach adjoining nodes. When you insert a bridge, the nodes are now not adjoining.
Lastly, we’ve got routers – Layer 3 gadgets that function on the community layer. Theoretically, any giant community (your private home Wi-Fi, a company LAN, or the worldwide Web) ought to use routers to interconnect segments.
Now that we all know which gadgets can carry out packet forwarding, let’s concentrate on two large questions:
-
Which system is aware of how one can ahead the packet?
In the event you’ve labored with IP, your intuition could be: “The router does!” However that’s just one forwarding paradigm. Generally, the sender determines the forwarding path—by deciding on a digital circuit, as an example—and gadgets within the community solely acknowledge these circuits. We’ll study at the very least three forwarding paradigms and establish which applied sciences, previous and current, use every.
For instance, section routing isn’t that totally different from source-route bridging in Token Ring. Nothing is really new in networking—we’ve simply reinvented concepts over time.
-
How does a tool know how one can ahead a packet?
No matter whether or not a tool is an finish node or an in-network system, it must get that info from someplace. It would guess, get it from a central controller, or study it from adjoining or non-adjacent gadgets.
The Three Planes of a Networking System
In any system that performs packet forwarding, there are three key planes:

-
Information Aircraft: That is the place the precise forwarding occurs. The system makes use of a forwarding desk to find out how one can ship a packet, primarily based on info like MAC addresses, IP addresses, MPLS labels, and so forth.
If the information airplane can’t deal with the packet—maybe it’s too complicated or destined for the system itself—it’s punted to the management airplane.
-
Management Aircraft consists of processes operating within the system’s OS (usually Linux or one other Unix-based system). These processes deal with duties like:
- Hyperlink Upkeep (e.g., utilizing BFD)
- Topology Discovery (dealt with by routing protocols like OSPF or IS-IS)
- Deal with Task (e.g., DHCP, SLAAC)
- Deal with Mapping (e.g., ARP for IPv4, Neighbor Discovery for IPv6)
-
Administration Aircraft handles configuration and monitoring. Within the outdated days, we used console cables to configure gadgets. At present, many gadgets boot from the community and are managed through SSH, Telnet, or APIs.
An honest system ought to help at the very least a CLI and an API, so it may be managed manually or through automation instruments.
Routing Protocols and the Forwarding Desk
Routing protocols—like OSPF, IS-IS, or BGP—run within the management airplane. They:
- Construct inner topology or route databases.
- Calculate routing tables.
- Mix routing info with knowledge hyperlink layer mappings to create the forwarding desk.
This forwarding desk is what the information airplane makes use of to effectively ahead packets.
Layer-2 vs Layer-3 Forwarding (And Advertising Confusion)
There are two main methods to ahead packets throughout a community:

Early bridges did layer-2 forwarding in software program and barely managed to cope with two 10 Mbps Ethernet ports. When distributors started implementing bridging in {hardware}, they coined the time period switching to distinguish between hardware- and software-based bridges. Later, when Layer 3 forwarding grew to become quick sufficient in {hardware}, we obtained Layer 3 switching. It was all advertising—designed to place merchandise in opposition to bigger rivals like Cisco.
In actuality, what’s the distinction between a router and a Layer 3 swap? Simply advertising. Efficiency, buffers, or options don’t outline it. The label is determined by what the seller needs to name the system.
Terminology Clarification
On this webinar, I’ll attempt to use constant terminology:
- Switching = any packet forwarding.
- Layer 2 Switching = forwarding primarily based on MAC addresses.
- Bridging = often refers to clear Ethernet bridging.
- Layer 3 Switching = forwarding primarily based on IP addresses (IPv4 or IPv6).
- Routing = path choice and management airplane actions associated to IP forwarding.
Q&A Highlights
Q: Are there any management airplane actions at Layer 2?
A: Virtually none. Clear bridges don’t run management airplane protocols between themselves and finish nodes. They depend on dynamic MAC studying within the knowledge airplane. Protocols like STP present primary loop prevention however provide minimal discovery or routing.
Q: Isn’t all switching able to routing as we speak?
A: Not at all times. Excessive-end knowledge heart switches usually help full IP routing. However in campus or industrial environments, you’ll nonetheless discover switches that want separate licenses for routing or solely help bridging.




